Screening for Spinal Muscular Atrophy, the Leading Genetic Cause of Infant Death, can Save Lives
Regina Philipps’ son, Shane, was born a happy, healthy, and strong baby – holding his head up on his own, rolling, and pushing himself up on his arms. But at six months old, Regina noticed something might be wrong.
“He started moving less, and some of the strength he had seemed to be disappearing,” said Regina. “It was subtle at first – like when he stopped grabbing my hands and pulling himself up after I changed his diaper. He got to the point where he couldn’t really move his legs. When sitting, he would fall over. He could barely even lift his arms up to his mouth to eat.”
Shane was diagnosed with spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) Type 2 – a progressive, rare genetic disease caused by the lack of a functional survival motor neuron 1 (SMN1) gene.1 Each year, one in every 11,000 babies is born with the disease.2,3 SMA is the leading genetic cause of infant death.1 SMA progresses quickly, meaning the earliest possible diagnosis and treatment is crucial. If left untreated in one of its most severe forms, Type 1, children often require permanent feeding and breathing support or pass away by their second birthday.4 While on average, babies with SMA Type 2 are diagnosed between six and 24 months of age, Shane received his diagnosis at 10 months old and he received treatment soon after.
Millions of babies across the country are routinely screened at birth for conditions that can affect a child’s long-term health or survival. In 2018, SMA was added to the Recommended Uniform Screening Panel (RUSP), a federal list of often devastating disorders that require intervention as early as possible and have treatment options available.5 Despite the fact there are now treatments approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for SMA, only 33 states screen for SMA through permanent or pilot programs, leaving babies in 17 states, plus Washington, D.C., unscreened for this devastating disease.5,6
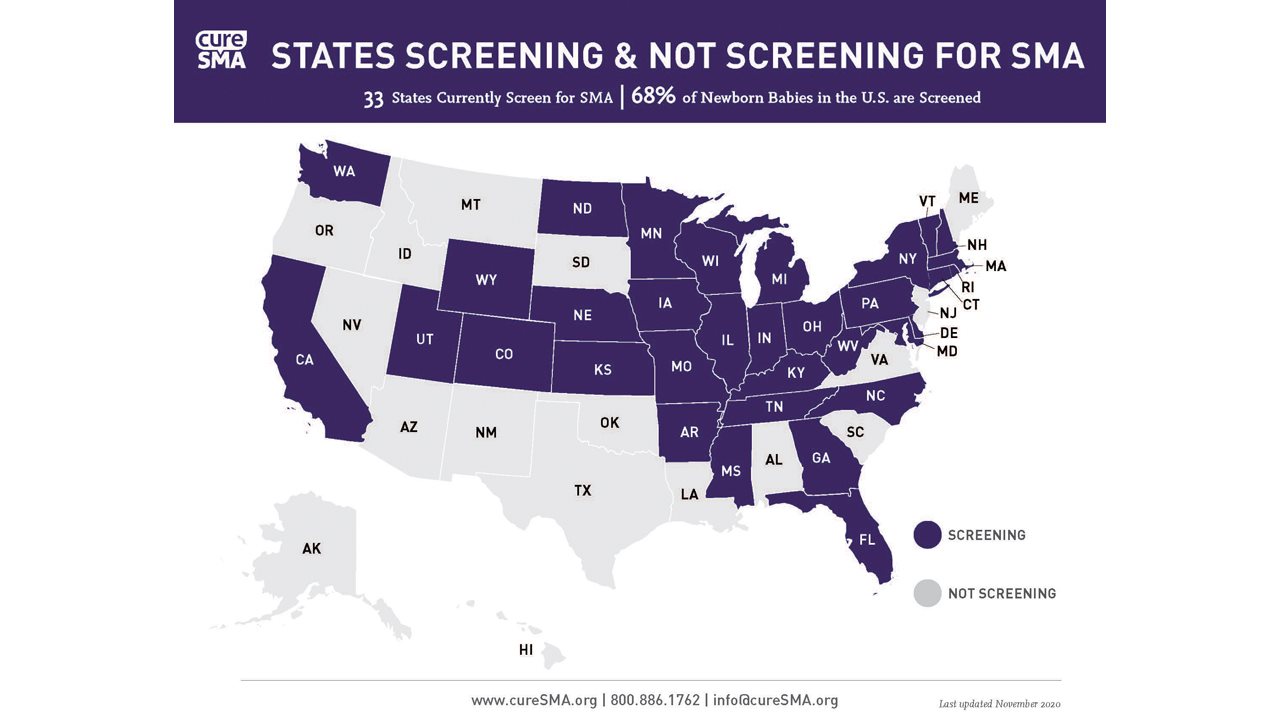
“We live in New Jersey, which was supposed to implement newborn screening for SMA this August, but because of the COVID-19 pandemic, is implementing it next year. Although we wish we knew sooner, we feel very lucky that Shane’s symptoms were caught relatively early and before he declined even further, so we could pursue treatment as fast as possible,” Regina said. “For babies like Shane, early diagnosis can mean prevention of disease progression. For some babies – especially those with SMA Type 1 – early diagnosis can mean the difference between life and death. That’s why I’m so passionate about educating on the importance of newborn screening, advancing efforts in my state and sharing how people can get involved.”
Children living in states with newborn screening in place can benefit from the remarkable difference early detection and treatment can make – an issue Rory and Carolyn Philstrom know firsthand. It wasn’t long before their son Edan was born that they moved from North Dakota to Minnesota, where Rory was due to start a new job. Because Minnesota actively conducts newborn screening for SMA, Edan’s pediatrician called five days after his birth to tell them his newborn screening test resulted in a positive diagnosis for SMA Type 1. They were blindsided by the diagnosis – but given how quickly SMA progresses, grateful that they could quickly work with their physician on a treatment plan – without losing the precious time they wouldn’t have benefited from in North Dakota. Without screening, children with SMA Type 1 typically receive a diagnosis anywhere up to 6 months after birth.
“Just the sooner you get the diagnosis – the sooner you get that phone call – can make a difference. Even days can make a difference,” said Carolyn.
Since Shane’s diagnosis, Regina has been an active member of the SMA community, helping to advocate for SMA to be added to her state’s newborn screening panel. Their efforts were successful and in January 2020, New Jersey passed a law to screen for SMA, which will be implemented in 2021. Other states have followed, including California, Illinois and Washington. By 2022, Regina, along with patients, caregivers, and the entire SMA community at large, are hopeful every newborn in the United States will be screened for this devastating disease. (BPT)
For more information about SMA and to inquire about what you can do to ensure that babies in your state are screened for this disease, visit CureSMA.org/ActionCenter.
References
- Anderton RS and Mastaglia FL. Expert Rev Neurother. 2015;15(8):895-908.
- Sugarman EA, et al. Eur J Hum Genet. 2012;20(1):27-32.
- Cure SMA. About SMA. https://www.curesma.org/about-sma/. Accessed June 21, 2020.
- Finkel RS, Finkel RS, et al. Neurology. 2014;83(9):810-817.
- Cure SMA. Newborn Screening for SMA. https://www.curesma.org/newborn-screening-for-sma/. Accessed November 18, 2020.
- Cure SMA. https://www.curesma.org/wpcontent/uploads/2020/02/SMA-State-Fact-Sheet_2020_DC_v3.pdf. Accessed November 18, 2020.




Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!